Omega-3 fatty acids have risen in popularity over the last few years, and it’s not without reason. The list of Omega-3 fish oil benefits and interesting tidbits could go on to fill a small library! That said, if you’re wondering how this important nutrient can help you specifically, you’re in the right place.
Table of Contents
The 16 Benefits of Omega-3 Fish Oil
Omega-3 is one of the most important nutrients our body needs to function properly. Whether you’re looking to boost your immune system, protect against chronic diseases, or enhance physical fitness, omega-3 can play a key role in maintaining overall well-being. Here’s how omega-3 can help you:
1. Balances omega-3 to omega-6 ratio
In a typical Western diet, omega-6 consumption tends to be higher than omega-3. Since omega-6 promotes inflammation and omega-3 reduces it, balancing these fatty acids is crucial for overall health.1 Increasing omega-3 intake helps restore this balance, benefiting heart health and reducing inflammation.
2. Anti-inflammatory effects
Omega-3’s key benefit is reducing inflammation by lowering pro-inflammatory cytokines.2 Chronic inflammation contributes to many diseases, including arthritis and heart disease. By controlling inflammation, omega-3 helps protect against these conditions and relieve symptoms of existing issues.
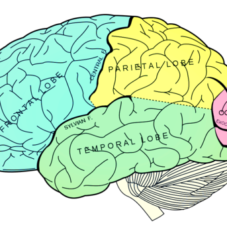
3. May offer neuroprotective benefits
DHA, a key omega-3 fatty acid, is a major structural component of brain cells and is essential for forming new neurons. Low DHA levels have been associated with cognitive challenges.3
Omega-3s may also help protect the nervous system from inflammation and support recovery from injuries or stress.4 Moreover, early intake has been linked to better cognitive development in children.3
4. May slow brain aging and neurodegeneration
Omega-3 fatty acids may help protect the brain as it ages, particularly in conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
In animal studies, omega-3 significantly reduced amyloid plaque buildup, which is commonly observed in the brains of individuals with Alzheimer’s.5 6 A 2018 systematic review also found that supplementation worked best in the earliest stages of the disease.7
Other studies show that omega-3 may help protect dopamine-producing brain cells by reducing inflammation, a factor believed to contribute to Parkinson’s progression.8 9 10 While more research is needed, these findings point to omega-3’s potential role in long-term brain health.

5. Helps with mood and focus
Researchers have studied omega-3 fatty acids (especially EPA and DHA) for their role in mental well-being. A meta-analysis of 26 studies involving over 2,000 participants found that omega-3 supplements improved depression symptoms.11 Other studies link low omega-3 levels to a higher risk of mood disorders.12
In children, omega-3s may influence brain development and behavior. Research shows that kids with ADHD often have lower omega-3 levels and reduced gray matter volume, which may impact focus and impulse control. While not a treatment, omega-3 supplementation may help manage common symptoms.13
6. Supports fertility and a healthy pregnancy
Omega-3 plays an important role in reproductive health for both men and women. During pregnancy, DHA helps support the developing baby’s brain and nervous system. Since fetal demand is high, pregnant women are more likely to become deficient.14 Research also suggests omega-3s may support healthy blood flow and help reduce the risk of complications like preeclampsia and preterm labor.15 16 17
For those trying to conceive, omega-3 may offer additional benefits. In women, it’s been studied for its role in hormone balance and inflammation – two major factors in PCOS and endometriosis.18 19
In men, research has linked omega-3 to improved sperm quality and motility, and it may help reduce the severity of varicocele, a common contributor to infertility.20 21
7. Plays a role in immune health
Fish oil benefits go beyond general wellness. As essential fats, omega-3s help regulate inflammation and support normal cell activity. Some evidence suggests they may also support people with autoimmune conditions like lupus or Crohn’s by reducing inflammation-related symptoms.2
On average, less medication was prescribed to those who included omega-3 in their diets. This helps cut down on negative side effects typically associated with prescription medications.2
8. May promote healthy skin and hair
Some studies suggest that omega-3s help the skin stay hydrated and may reduce inflammation linked to sun exposure and conditions like psoriasis. In one study, 80% of people with psoriasis reported symptom improvement after supplementing with omega-3.22 23
Additionally, research on female pattern hair loss found that regular supplementation was linked to reduced hair shedding, improved hair density, and shinier strands over time.24
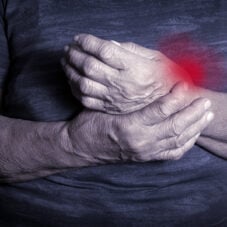
9. Manages rheumatoid arthritis symptoms
Omega-3 has a positive effect on autoimmune disorders, but it appears to be exceptionally beneficial to those with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Studies have shown that omega-3 can increase anti-inflammatory compounds in both RA patients and healthy individuals. This anti-inflammatory effect helps reduce joint inflammation, stiffness, and tenderness.25 26
10. Omega-3 supports bone health
Getting enough omega-3, particularly DHA, during youth could lead to stronger, healthier bones. Higher levels of omega-3 in the blood were associated with greater mineral bone density. Omega-3 is important for long-term bone health and also reduces the risk of bone conditions like osteoporosis later in life.27 28
11. Might lessen the severity of asthma
Asthma patients often have lower omega-3 levels and higher omega-6 levels, with the latter linked to more severe symptoms. This imbalance may contribute to asthma severity. Studies suggest that omega-3 has a protective effect, reducing the intensity of asthma attacks and improving respiratory capacity, which may result in fewer attacks.29
12. Promotes good eye health
Much like with the brain, omega-3 is a building block for the formation of the eyes. Beyond development, omega-3 also supports eye health by aiding the meibomian glands, which produce protective oils to keep eyes from drying out. Omega-3 helps prevent inflammation that can damage these glands, reducing the risk of dry eyes.30

13. Promotes heart health
Omega-3 fatty acids are widely recognized for their heart-friendly benefits.
According to the American Heart Association, omega-3s help maintain heart function and support overall vascular health.31 They may also help lower blood pressure in people with hypertension.32
14. Reduces the risk of diabetes
Fish oil benefits may include reducing the risk of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. In studies, omega-3 was found to prevent islet autoimmunity, which can lead to Type 1 diabetes in children.33
For Type 2 diabetes, which is often caused by obesity, omega-3 can also be helpful. In combination with exercise, omega-3 helps regulate appetite and supports weight loss. This can lower the risk of developing obesity-related diabetes.34
15. Improves lipid profile
Your lipid profile includes triglycerides, cholesterol, and lipoproteins like VLDL (very low-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), and HDL (high-density lipoprotein). High levels of VLDL and LDL are linked to heart issues, while HDL helps regulate them.35
Omega-3 improves the lipid profile by reducing triglycerides, which lowers VLDL and LDL. It also decreases apolipoprotein B, a protein that forms VLDL and LDL. Omega-3 only slightly raises the amount of HDL so its main benefit is the reduction of the more trouble-causing lipoproteins.36
16. Enhances exercise performance
Omega-3 can help you maximize the benefits of your workouts. It reduces cortisol, a hormone that can hinder muscle growth, and boosts muscle protein synthesis.37
Omega-3 also improves blood flow, which then prevents mid-workout fatigue and allows you to exercise longer. Additionally, by providing good blood flow and reducing inflammation, omega-3 can ease post-workout soreness. This means you get to recover from a strenuous workout more quickly.38
How to enjoy all these Omega-3 fish oil benefits?
While a balanced diet should be enough, most people don’t get the recommended levels from food alone. That’s where Ultra Pure Omega-3 Fish Oil softgels come in. Our high-quality fish oil supplement makes it easy to get optimal amounts of EPA and DHA. To be exact, each 3-softgel serving provides 2,250 mg of omega-3 fatty acids, without the fishy aftertaste!
Conclusion
Omega-3 offers a broad range of health benefits, from reducing inflammation and improving brain and heart health to supporting exercise performance. Incorporating more omega-3 into your diet, whether through fatty fish or our Ultra Pure Omega-3 supplement, can provide lasting positive effects for your body and mind.
💬 Got questions about Omega-3? Drop a comment below, we’d love to hear from you!
📩 And while you’re here, join our newsletter for more smart stuff (and secret perks)!
References:
- Ap, Simopoulos. “The Importance of the Ratio of Omega-6/Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids.” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie, 1 Oct. 2002, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12442909/. ↩︎
- Simopoulos, Artemis P. “Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Inflammation and Autoimmune Diseases.” Journal of the American College of Nutrition, vol. 21, no. 6, Dec. 2002, pp. 495–505, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12480795/ ↩︎
- Singh, Meharban. “Essential Fatty Acids, DHA and Human Brain.” Indian Journal of Pediatrics, vol. 72, no. 3, 1 Mar. 2005, pp. 239–242, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15812120/ ↩︎
- Simopoulos, Artemis P. “Omega-6/Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acid Ratio and Chronic Diseases.” Food Reviews International, vol. 20, no. 1, 2004, pp. 77–90, https://doi.org/10.1081/fri-120028831 ↩︎
- Jicha, Greg. “Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Potential Role in the Management of Early Alzheimer’s Disease.” Clinical Interventions in Aging, Mar. 2010, p. 45, https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.s5231 ↩︎
- Lim, G. P. “A Diet Enriched with the Omega-3 Fatty Acid Docosahexaenoic Acid Reduces Amyloid Burden in an Aged Alzheimer Mouse Model.” Journal of Neuroscience, vol. 25, no. 12, 23 Mar. 2005, pp. 3032–3040, https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4225-04.2005. ↩︎
- Canhada, Scheine, et al. “Omega-3 Fatty Acids’ Supplementation in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review.” Nutritional Neuroscience, vol. 21, no. 8, 3 May 2017, pp. 529–538, https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415x.2017.1321813. ↩︎
- Bousquet, M., et al. “Beneficial Effects of Dietary Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid on Toxin-Induced Neuronal Degeneration in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease.” The FASEB Journal, vol. 22, no. 4, Apr. 2008, pp. 1213–1225, https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.07-9677com. ↩︎
- Delattre, Ana Marcia, et al. “Evaluation of Chronic Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation on Behavioral and Neurochemical Alterations in 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesion Model of Parkinson’s Disease.” Neuroscience Research, vol. 66, no. 3, Mar. 2010, pp. 256–264, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2009.11.006. ↩︎
- “Parkinson’s Severity Linked to Brain Inflammation.” Www.medicalnewstoday.com, 29 Aug. 2013, www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/265378. ↩︎
- Liao, Yuhua, et al. “Efficacy of Omega-3 PUFAs in Depression: A Meta-Analysis.” Translational Psychiatry, vol. 9, no. 1, 5 Aug. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0515-5 ↩︎
- Lange, Klaus W. “Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Mental Health.” Global Health Journal, vol. 4, no. 1, Mar. 2020, pp. 18–30, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.glohj.2020.01.004. ↩︎
- Sinn, Natalie, and Janet Bryan. “Effect of Supplementation with Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Micronutrients on Learning and Behavior Problems Associated with Child ADHD.” Journal of Developmental & Behavioral Pediatrics, vol. 28, no. 2, Apr. 2007, pp. 82–91, https://doi.org/10.1097/01.dbp.0000267558.88457.a5 ↩︎
- Carlson, Susan E, et al. “DHA Supplementation and Pregnancy Outcomes123.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol. 97, no. 4, 1 Apr. 2013, pp. 808–815, https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.112.050021. ↩︎
- Lazzarin, Natalia, et al. “Low-Dose Aspirin and Omega-3 Fatty Acids Improve Uterine Artery Blood Flow Velocity in Women with Recurrent Miscarriage due to Impaired Uterine Perfusion.” Fertility and Sterility, vol. 92, no. 1, July 2009, pp. 296–300, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.05.045. ↩︎
- Qiu, Chunfang, et al. “Erythrocyte Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Preeclampsia Risk in Peruvian Women.” Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics, vol. 274, no. 2, 7 Mar. 2006, pp. 97–103, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-006-0140-4. ↩︎
- Olsen, S.F., et al. “Randomised Controlled Trial of Effect of Fish-Oil Supplementation on Pregnancy Duration.” The Lancet, vol. 339, no. 8800, Apr. 1992, pp. 1003–1007, https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(92)90533-9. ↩︎
- Oner, G., and I. I. Muderris. “Efficacy of Omega-3 in the Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.” Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, vol. 33, no. 3, Apr. 2013, pp. 289–291, https://doi.org/10.3109/01443615.2012.751365. ↩︎
- Tomio, Kensuke, et al. “Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Suppress the Cystic Lesion Formation of Peritoneal Endometriosis in Transgenic Mouse Models.” PLoS ONE, vol. 8, no. 9, 10 Sept. 2013, p. e73085, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073085. ↩︎
- Safarinejad, M. R. “Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Semen Profile and Enzymatic Anti-Oxidant Capacity of Seminal Plasma in Infertile Men with Idiopathic Oligoasthenoteratospermia: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomised Study.” Andrologia, vol. 43, no. 1, 19 Dec. 2010, pp. 38–47, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0272.2009.01013.x. ↩︎
- Tang, Li-Xin, et al. “Association of Decreased Spermatozoa Omega-3 Fatty Acid Levels and Increased Oxidative DNA Damage with Varicocele in Infertile Men: A Case Control Study.” Reproduction, Fertility and Development, vol. 28, no. 5, 2016, p. 648, https://doi.org/10.1071/rd14276. ↩︎
- Rhodes, Lesley E., et al. “Dietary Fish Oil Reduces Basal and Ultraviolet B-Generated PGE2 Levels in Skin and Increases the Threshold to Provocation of Polymorphic Light Eruption.” Journal of Investigative Dermatology, vol. 105, no. 4, 1 Oct. 1995, pp. 532–535, https://doi.org/10.1111/1523-1747.ep12323389 ↩︎
- Maurice, P.D.L, et al. The Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Fish Oil in Patients with Psoriasis. Vol. 117, no. 5, 1 Nov. 1987, pp. 599–606, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.1987.tb07492.x. ↩︎
- Le Floc’h, Caroline, et al. “Effect of a Nutritional Supplement on Hair Loss in Women.” Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, vol. 14, no. 1, 8 Jan. 2015, pp. 76–82, https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12127. ↩︎
- Akbar, Umair, et al. “Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Rheumatic Diseases.” JCR: Journal of Clinical Rheumatology, vol. 23, no. 6, Sept. 2017, pp. 330–339, https://doi.org/10.1097/rhu.0000000000000563. ↩︎
- Tański, Wojciech, et al. “The Relationship between Fatty Acids and the Development, Course and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.” Nutrients, vol. 14, no. 5, 28 Feb. 2022, p. 1030, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14051030. ↩︎
- Högström, Magnus, et al. “N−3 Fatty Acids Are Positively Associated with Peak Bone Mineral Density and Bone Accrual in Healthy Men: The NO2 Study.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol. 85, no. 3, 1 Mar. 2007, pp. 803–807, https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/85.3.803. ↩︎
- Elbahnasawy, Amr Samir, et al. “Protective Effect of Dietary Oils Containing Omega-3 Fatty Acids against Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis.” Journal of Nutrition and Health, vol. 52, no. 4, 2019, p. 323, https://doi.org/10.4163/jnh.2019.52.4.323. ↩︎
- Oddy, W. H., et al. “Ratio of Omega‐6 to Omega‐3 Fatty Acids and Childhood Asthma.” Journal of Asthma, vol. 41, no. 3, Jan. 2004, pp. 319–326, https://doi.org/10.1081/jas-120026089. ↩︎
- Macsai, Marian S. “The Role of Omega-3 Dietary Supplementation in Blepharitis and Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (an AOS Thesis).” Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society, vol. 106, 2008, pp. 336–356, pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19277245/. ↩︎
- Siscovick, David S., et al. “Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid (Fish Oil) Supplementation and the Prevention of Clinical Cardiovascular Disease.” Circulation, vol. 135, no. 15, 11 Apr. 2017, https://doi.org/10.1161/cir.0000000000000482. ↩︎
- Li, Jianjun, et al. “Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Consensus Statement from the Experts’ Committee of National Society of Cardiometabolic Medicine.” Frontiers in Pharmacology, vol. 13, 12 Dec. 2022, https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1069992 ↩︎
- Norris, Jill M., et al. “Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake and Islet Autoimmunity in Children at Increased Risk for Type 1 Diabetes.” JAMA, vol. 298, no. 12, 26 Sept. 2007, p. 1420, https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.298.12.1420. ↩︎
- Parra, Dolores, et al. “A Diet Rich in Long Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids Modulates Satiety in Overweight and Obese Volunteers during Weight Loss.” Appetite, vol. 51, no. 3, Nov. 2008, pp. 676–680, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2008.06.003. ↩︎
- Illingworth, D. R., et al. “Inhibition of Low Density Lipoprotein Synthesis by Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Humans.” Arteriosclerosis (Dallas, Tex.), vol. 4, no. 3, 1984, pp. 270–275, https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atv.4.3.270. ↩︎
- Skulas-Ray, Ann C., et al. “Dose-Response Effects of Marine Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Apolipoproteins, Apolipoprotein-Defined Lipoprotein Subclasses, and Lp-PLA2 in Individuals with Moderate Hypertriglyceridemia.” Journal of Clinical Lipidology, vol. 9, no. 3, May 2015, pp. 360–367, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacl.2014.12.001. ↩︎
- Smith, Gordon I, et al. “Dietary Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Increases the Rate of Muscle Protein Synthesis in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol. 93, no. 2, 15 Dec. 2010, pp. 402–412, https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.110.005611. ↩︎
- Noreen, Eric E, et al. “Effects of Supplemental Fish Oil on Resting Metabolic Rate, Body Composition, and Salivary Cortisol in Healthy Adults.” Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, vol. 7, 8 Oct. 2010, p. 31, https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-7-31. ↩︎